Data components in Langflow
Data components load data from a source into your flow.
They may perform some processing or type checking, like converting raw HTML data into text, or ensuring your loaded file is of an acceptable type.
Use data components in a flow
Components like News search, RSS reader, and Web search all fetch data into Langflow, and connect to Langflow in the same way. They can output the retrieved data in DataFrame format, or can be connected to an Agent component to be used as tools.
For example, to connect all three components to an Agent component, do the following:
- Create the Simple Agent starter flow.
- In the Agent component, in the OpenAI API Key field, add your OpenAI API key.
- Add the News search, RSS reader, and Web Search components to your flow.
- In all three components, enable Tool Mode.
- Connect the three components to the Agent component's Tools port. The flow looks like the following:
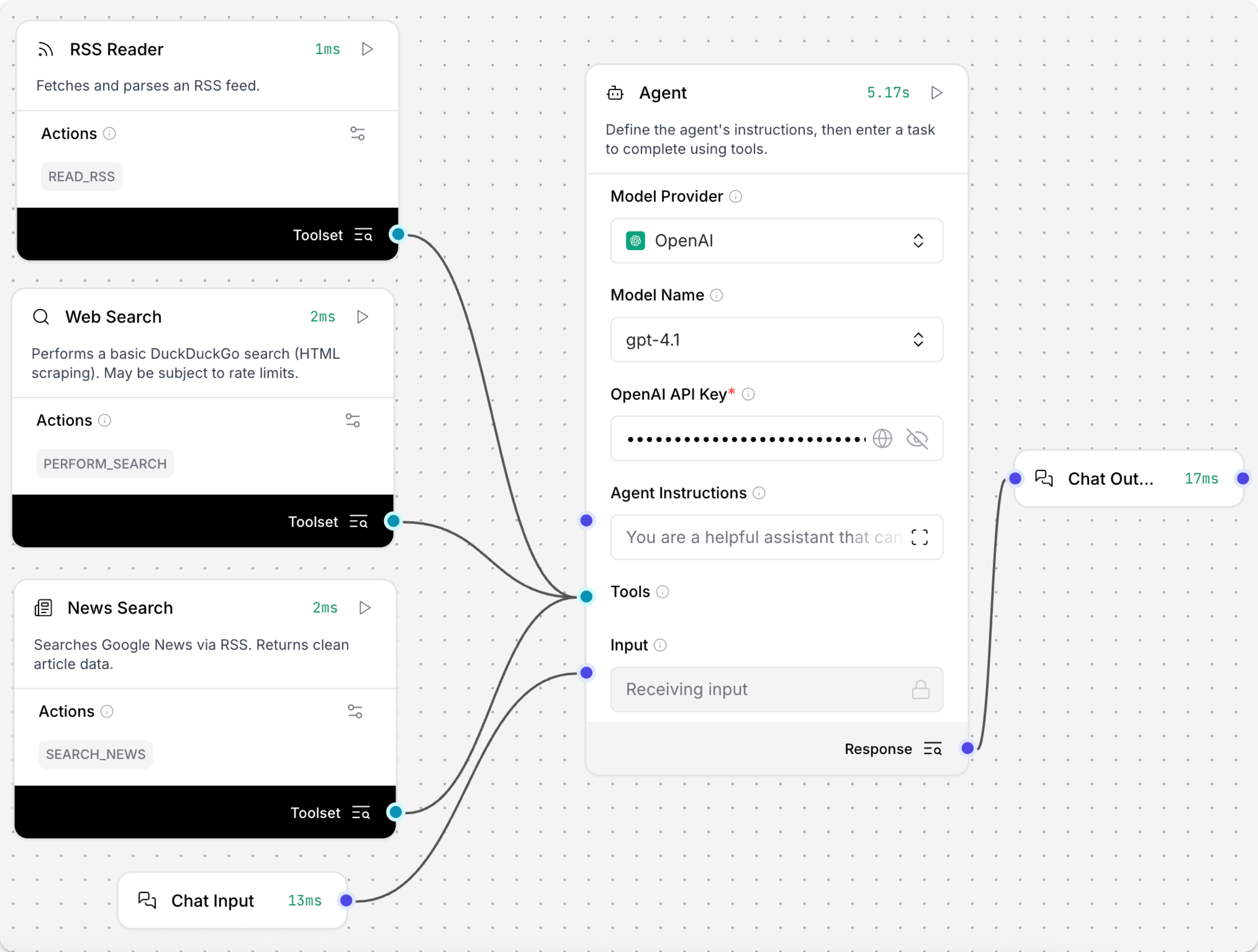
- Open the Playground and enter
Use the websearch component to get me an RSS feed of the latest news.The Agent uses theperform_searchtool to return a list of RSS feeds. - Enter the name of an RSS feed that interests you.
The Agent uses the
read_rsstool to fetch and summarize the latest RSS feed.
API Request
This component makes HTTP requests using URLs or cURL commands.
-
To use this component in a flow, connect the Data output to a component that accepts the input. For example, connect the API Request component to a Chat Output component.
-
In the API component's URLs field, enter the endpoint for your request. This example uses
https://dummy-json.mock.beeceptor.com/posts, which is a list of technology blog posts. -
In the Method field, enter the type of request. This example uses GET to retrieve a list of blog posts. The component also supports POST, PATCH, PUT, and DELETE.
-
Optionally, enable the Use cURL button to create a field for pasting curl requests. The equivalent call in this example is
curl -v https://dummy-json.mock.beeceptor.com/posts. -
Click Playground, and then click Run Flow. Your request returns a list of blog posts in the
resultfield.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| urls | URLs | Enter one or more URLs, separated by commas. |
| curl | cURL | Paste a curl command to populate the dictionary fields for headers and body. |
| method | Method | The HTTP method to use. |
| use_curl | Use cURL | Enable cURL mode to populate fields from a cURL command. |
| query_params | Query Parameters | The query parameters to append to the URL. |
| body | Body | The body to send with the request as a dictionary (for POST, PATCH, PUT). |
| headers | Headers | The headers to send with the request as a dictionary. |
| timeout | Timeout | The timeout to use for the request. |
| follow_redirects | Follow Redirects | Whether to follow http redirects. |
| save_to_file | Save to File | Save the API response to a temporary file. |
| include_httpx_metadata | Include HTTPx Metadata | Include properties such as headers, status_code, response_headers, and redirection_history in the output. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| data | Data | The result of the API requests. Returns a Data object containing source URL and results. |
| dataframe | DataFrame | Converts the API response data into a tabular DataFrame format. |
Directory
This component recursively loads files from a directory, with options for file types, depth, and concurrency.
Parameters
Inputs
| Input | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| path | MessageTextInput | The path to the directory to load files from. |
| types | MessageTextInput | The file types to load (leave empty to load all types). |
| depth | IntInput | The depth to search for files. |
| max_concurrency | IntInput | The maximum concurrency for loading files. |
| load_hidden | BoolInput | If true, hidden files are loaded. |
| recursive | BoolInput | If true, the search is recursive. |
| silent_errors | BoolInput | If true, errors do not raise an exception. |
| use_multithreading | BoolInput | If true, multithreading is used. |
Outputs
| Output | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data | List[Data] | The loaded file data from the directory. |
| dataframe | DataFrame | The loaded file data in tabular DataFrame format. |
File
This component loads and parses files of various supported formats and converts the content into a Data object. It supports multiple file types and provides options for parallel processing and error handling.
To load a document, follow these steps:
- Click the Select files button.
- Select a local file or a file loaded with File management, and then click Select file.
The loaded file name appears in the component.
The default maximum supported file size is 100 MB. To modify this value, see --max-file-size-upload.
The File component’s outputs change dynamically based on the number and type of files you select. For more information, expand the following Parameters section, and then review the Outputs parameters.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| path | Files | The path to files to load. Supports individual files or bundled archives. |
| file_path | Server File Path | A Data object with a file_path property pointing to the server file or a Message object with a path to the file. Supersedes 'Path' but supports the same file types. |
| separator | Separator | The separator to use between multiple outputs in Message format. |
| silent_errors | Silent Errors | If true, errors do not raise an exception. |
| delete_server_file_after_processing | Delete Server File After Processing | If true, the Server File Path is deleted after processing. |
| ignore_unsupported_extensions | Ignore Unsupported Extensions | If true, files with unsupported extensions are not processed. |
| ignore_unspecified_files | Ignore Unspecified Files | If true, Data with no file_path property is ignored. |
| use_multithreading | [Deprecated] Use Multithreading | Set 'Processing Concurrency' greater than 1 to enable multithreading. This option is deprecated. |
| concurrency_multithreading | Processing Concurrency | When multiple files are being processed, the number of files to process concurrently. Default is 1. Values greater than 1 enable parallel processing for 2 or more files. |
Outputs
The outputs change dynamically based on the number and type of files selected.
If a single file is selected:
- Structured Content DataFrame: If a CSV or Excel file is selected, the component outputs tabular data.
- Structured Content Data: If a JSON file is selected, the component outputs parsed JSON data.
- Raw Content Message: Outputs the file's raw text content.
- File Path Message: Outputs the path to the file on the Langflow server.
If multiple files are selected:
- Files DataFrame: A table containing the content and metadata of all selected files.
If no files are selected:
- No outputs are displayed.
Supported File Types
Text files:
.txt- Text files.md,.mdx- Markdown files.csv- CSV files.json- JSON files.yaml,.yml- YAML files.xml- XML files.html,.htm- HTML files.pdf- PDF files.docx- Word documents.py- Python files.sh- Shell scripts.sql- SQL files.js- JavaScript files.ts,.tsx- TypeScript files
Archive formats (for bundling multiple files):
.zip- ZIP archives.tar- TAR archives.tgz- Gzipped TAR archives.bz2- Bzip2 compressed files.gz- Gzip compressed files
News search
This component searches Google News with RSS and returns clean article data. The clean_html method parses the HTML content with the BeautifulSoup library, and then removes HTML markup and strips whitespace so the output data is clean.
It returns news content as a DataFrame containing article titles, links, publication dates, and summaries. The component can also be used in Tool Mode with a connected Agent.
To use this component in a flow, connect the News Search output to a component that accepts the DataFrame input. For example, connect the News Search component to a Chat Output component. Enter a search query, open the Playground, and click Run Flow.
The latest content is returned in a structured DataFrame, with the key columns title, link, published and summary.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| query | Search Query | Search keywords for news articles. |
| hl | Language (hl) | Language code, such as en-US, fr, de. Default: en-US. |
| gl | Country (gl) | Country code, such as US, FR, DE. Default: US. |
| ceid | Country:Language (ceid) | Language, such as US:en, FR:fr. Default: US:en. |
| topic | Topic | One of: WORLD, NATION, BUSINESS, TECHNOLOGY, ENTERTAINMENT, SCIENCE, SPORTS, HEALTH. |
| location | Location (Geo) | City, state, or country for location-based news. Leave blank for keyword search. |
| timeout | Timeout | Timeout for the request in seconds. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| articles | News Articles | A DataFrame containing article titles, links, publication dates, and summaries. |
RSS Reader
This component fetches and parses RSS feeds from any valid RSS feed URL. It returns the feed content as a DataFrame containing article titles, links, publication dates, and summaries. The component can also be used in Tool Mode with a connected Agent.
To use this component in a flow, do the following:
- Connect the RSS reader output to a component that accepts the DataFrame input, such as a Chat Output component.
- In the RSS Feed URL field, enter an RSS feed, such as
https://rss.nytimes.com/services/xml/rss/nyt/HomePage.xmlfor the New York Times. - Open the Playground, and then click Run Flow.
The latest content is returned in a structured DataFrame, with the key columns title, link, published and summary.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| rss_url | RSS Feed URL | URL of the RSS feed to parse. |
| timeout | Timeout | Timeout for the RSS feed request in seconds. Default: 5. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| articles | Articles | A DataFrame containing article titles, links, publication dates, and summaries. |
SQL database
This component executes SQL queries on SQLAlchemy-compatible databases. It supports any SQLAlchemy-compatible database, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, and others.
To use this component in a flow, do the following:
- Create a test database called
test.db.
_10sqlite3 test.db
- Add values to the test database.
_10sqlite3 test.db "CREATE TABLE users (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, email TEXT, age INTEGER); INSERT INTO users (name, email, age) VALUES ('John Doe', 'john@example.com', 30), ('Jane Smith', 'jane@example.com', 25), ('Bob Johnson', 'bob@example.com', 35);"
- Verify that
test.dbhas been created and contains your data.
_10sqlite3 test.db "SELECT * FROM users;"
Result:
_101|John Doe|john@example.com_102|Jane Smith|jane@example.com_103|John Doe|john@example.com_104|Jane Smith|jane@example.com
- In the SQL Database component's Database URL field, add the connection string for
test.db, such assqlite:///test.db.
With this connection established, the SQL Query field now accepts SQL queries. Instead of manually entering SQL queries, connect this database to an agent as a Tool to query it with natural language.
- In the SQL Database component, enable Tool Mode, and then connect it to an Agent component. The flow looks like the following:
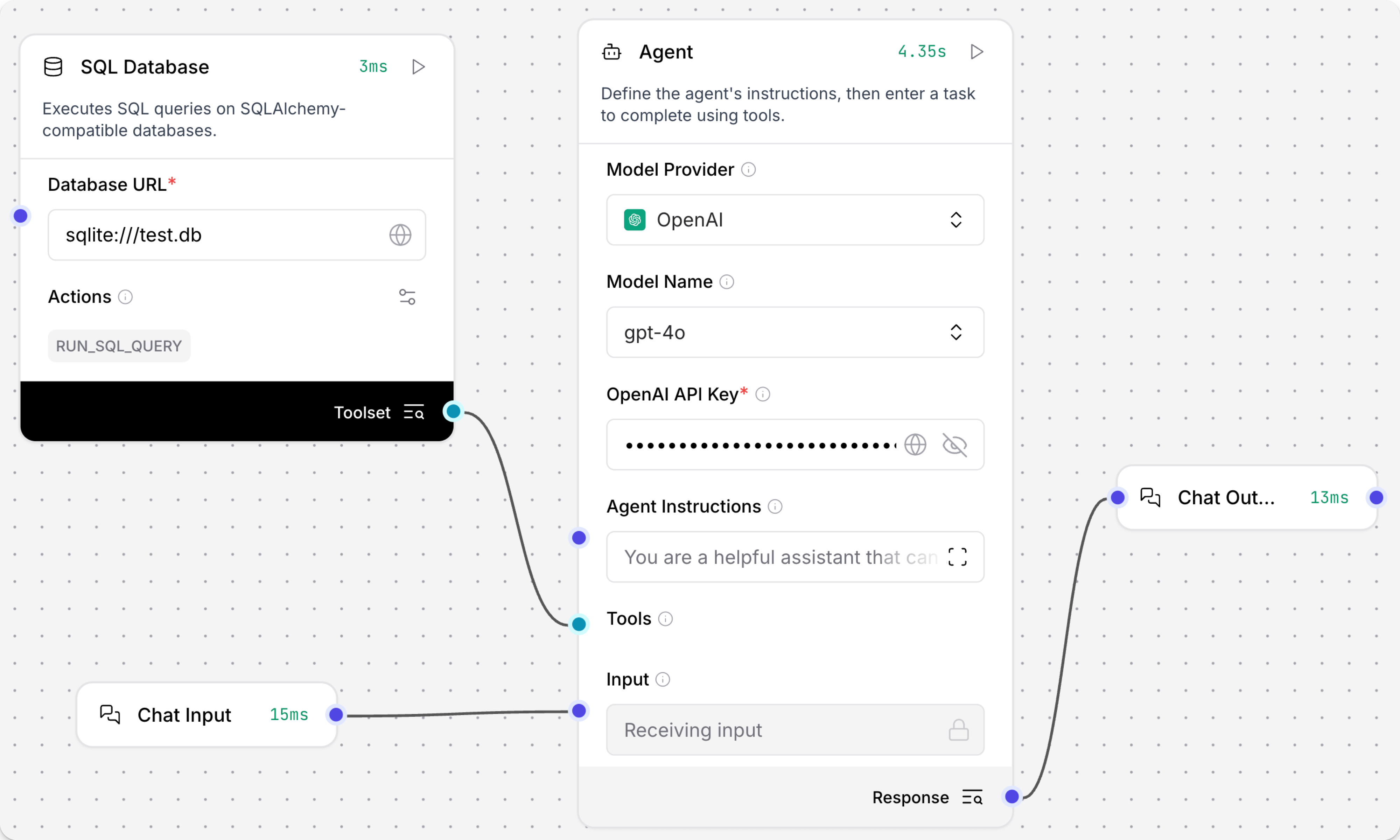
- In the Agent component, in the OpenAI API Key field, add your OpenAI API key.
- Open the Playground and ask
What users are in my database?The Agent uses therun_sql_querytool to retrieve the information, and additionally identifies the duplicateusersentries.
Result:
_10Here are the users in your database:_10_101. **John Doe** - Email: john@example.com_102. **Jane Smith** - Email: jane@example.com_103. **John Doe** - Email: john@example.com_104. **Jane Smith** - Email: jane@example.com_10_10It seems there are duplicate entries for the users._10_10> Finished chain.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| database_url | Database URL | The SQLAlchemy-compatible database connection URL. |
| query | SQL Query | The SQL query to execute. |
| include_columns | Include Columns | If enabled, includes column names in the result. Default: true. |
| add_error | Add Error | If enabled, adds any error messages to the result. Default: false. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| run_sql_query | Result Table | The query results as a DataFrame. |
Web search
This component performs web searches using DuckDuckGo's HTML interface, and returns the search results as a DataFrame containing the key columns title, links, and snippets. The component can also be used in Tool Mode with a connected Agent.
To use this component in a flow, do the following:
- Add the Web search component to the Basic prompting flow. In the Search Query field, enter a query, such as
environmental news. - Connect the Web search component's output to a component that accepts the DataFrame input.
- Connect a Type Convert component to convert the DataFrame to a Message.
- In the Type Convert component, in the Output Type field, select Message. Your flow looks like the following:
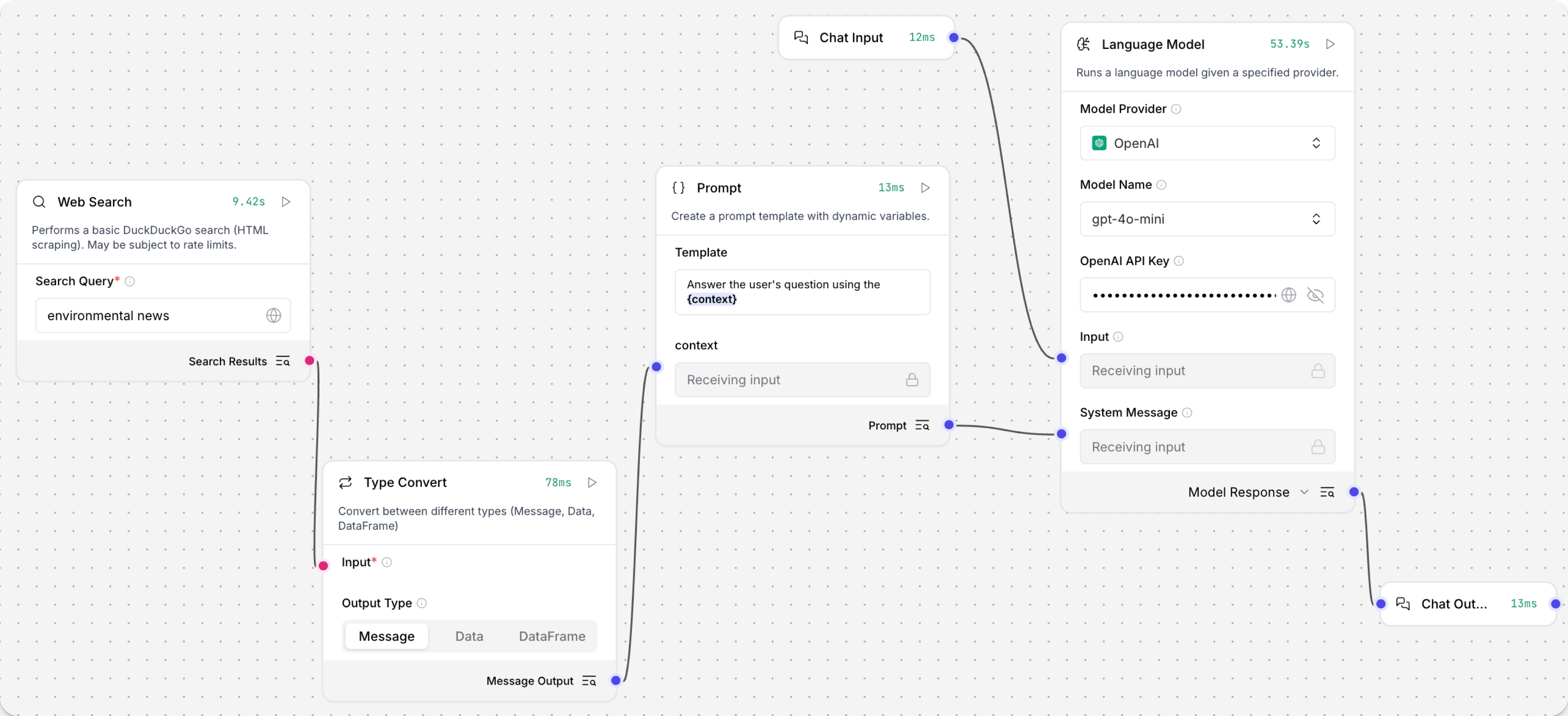
- In the Language Model component, in the OpenAI API Key field, add your OpenAI API key.
- Click Playground, and then ask about
latest news.
The search results are returned to the Playground as a message.
Result:
_10Latest news_10AI_10gpt-4o-mini_10Here are some of the latest news articles related to the environment:_10Ozone Pollution and Global Warming: A recent study highlights that ozone pollution is a significant global environmental concern, threatening human health and crop production while exacerbating global warming. Read more_10...
This component uses web scraping and may be subject to rate limits. For production use, consider using an official search API.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| query | Search Query | Keywords to search for. |
| timeout | Timeout | Timeout for the web search request in seconds. Default: 5. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| results | Search Results | A DataFrame containing search results with titles, links, and snippets. |
URL
This component fetches content from one or more URLs, processes the content, and returns it in various formats. It supports output in plain text or raw HTML.
In the component's URLs field, enter the URL you want to load. To add multiple URL fields, click Add URL.
-
To use this component in a flow, connect the DataFrame output to a component that accepts the input. For example, connect the URL component to a Chat Output component.
-
In the URL component's URLs field, enter the URL for your request. This example uses
langflow.org. -
Optionally, in the Max Depth field, enter how many pages away from the initial URL you want to crawl. Select
1to crawl only the page specified in the URLs field. Select2to crawl all pages linked from that page. The component crawls by link traversal, not by URL path depth. -
Click Playground, and then click Run Flow. The text contents of the URL are returned to the Playground as a structured DataFrame.
-
In the URL component, change the output port to Message, and then run the flow again. The text contents of the URL are returned as unstructured raw text, which you can extract patterns with the Parser component.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| urls | URLs | Click the '+' button to enter one or more URLs to crawl recursively. |
| max_depth | Max Depth | Controls how many 'clicks' away from the initial page the crawler will go. |
| prevent_outside | Prevent Outside | If enabled, only crawls URLs within the same domain as the root URL. |
| use_async | Use Async | If enabled, uses asynchronous loading which can be significantly faster but might use more system resources. |
| format | Output Format | Output Format. Use Text to extract the text from the HTML or HTML for the raw HTML content. |
| timeout | Timeout | Timeout for the request in seconds. |
| headers | Headers | The headers to send with the request. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| data | Data | A list of Data objects containing fetched content and metadata. |
| text | Message | The fetched content as formatted text. |
| dataframe | DataFrame | The content formatted as a DataFrame object. |
Webhook
This component defines a webhook trigger that runs a flow when it receives an HTTP POST request.
If the input is not valid JSON, the component wraps it in a payload object so that it can be processed and still trigger the flow.
When a Webhook component is added to the workspace, a new Webhook cURL tab becomes available in the API pane that contains an HTTP POST request for triggering the webhook component. For example:
Replace LANGFLOW_SERVER_ADDRESS, FLOW_ID, and LANGFLOW_API_KEY with the values from your Langflow deployment.
_10curl -X POST \_10 "http://LANGFLOW_SERVER_ADDRESS/api/v1/webhook/FLOW_ID" \_10 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \_10 -H 'x-api-key: LANGFLOW_API_KEY' \_10 -d '{"any": "data"}'
The Webhook component is often paired with a Parser component to extract relevant data from the raw payload. For more information, see Trigger flows with webhooks.
To troubleshoot a flow with a Webhook component and verify that the component is receiving data, you can create a small flow that outputs only the parsed payload:
-
Create a flow with Webhook, Parser, and Chat Output components.
-
Connect the Webhook component's Data output to the Parser component's Data input.
-
Connect the Parser component's Parsed Text output to the Chat Output component's Text input.
-
Edit the Parser component to set Mode to Stringify.
This mode passes the data received by the Webhook component as a string that is printed by the Chat Output component.
-
Click Share, select API access, and then copy the Webhook cURL code snippet.
-
Optional: Edit the
datain the code snippet if you want to pass a different payload. -
Send the POST request to trigger the flow.
-
Click Playground to verify that the Chat Output component printed the JSON data from your POST request.
For more information, see Trigger flows with webhooks.
Parameters
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data | Payload | Receives a payload from external systems through HTTP POST requests. |
| curl | cURL | The cURL command template for making requests to this webhook. |
| endpoint | Endpoint | The endpoint URL where this webhook receives requests. |
Outputs
| Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| output_data | Data | Outputs processed data from the webhook input, and returns an empty Data object if no input is provided. If the input is not valid JSON, the component wraps it in a payload object. |
Legacy components
Legacy components are available for use but are no longer supported.
Gmail Loader
This component loads emails from Gmail using provided credentials and filters.
For more information about creating a service account JSON, see Service Account JSON.
Parameters
Inputs
| Input | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| json_string | SecretStrInput | A JSON string containing OAuth 2.0 access token information for service account access. |
| label_ids | MessageTextInput | A comma-separated list of label IDs to filter emails. |
| max_results | MessageTextInput | The maximum number of emails to load. |
Outputs
| Output | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data | Data | The loaded email data. |
Google Drive Loader
This component loads documents from Google Drive using provided credentials and a single document ID.
For more information about creating a service account JSON, see Service Account JSON.
Parameters
Inputs
| Input | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| json_string | SecretStrInput | A JSON string containing OAuth 2.0 access token information for service account access. |
| document_id | MessageTextInput | A single Google Drive document ID. |
Outputs
| Output | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| docs | Data | The loaded document data. |
Google Drive Search
This component searches Google Drive files using provided credentials and query parameters.
For more information about creating a service account JSON, see Service Account JSON.
Parameters
Inputs
| Input | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| token_string | SecretStrInput | A JSON string containing OAuth 2.0 access token information for service account access. |
| query_item | DropdownInput | The field to query. |
| valid_operator | DropdownInput | The operator to use in the query. |
| search_term | MessageTextInput | The value to search for in the specified query item. |
| query_string | MessageTextInput | The query string used for searching. |
Outputs
| Output | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| doc_urls | List[str] | The URLs of the found documents. |
| doc_ids | List[str] | The IDs of the found documents. |
| doc_titles | List[str] | The titles of the found documents. |
| Data | Data | The document titles and URLs in a structured format. |