Language Model
Language model components in Langflow generate text using a specified Large Language Model (LLM). These components accept inputs like chat messages, files, and instructions in order to generate a text response.
Langflow includes a Language Model core component that has built-in support for many LLMs. Alternatively, you can use any additional language model in place of the Language Model core component.
Use language model components in flows
Use language model components anywhere you would use an LLM in a flow.
- Chat
- Drivers
- Agents
One of the most common use cases of language model components is to chat with LLMs in your flows.
The following example uses a language model component in a chatbot flow similar to the Basic Prompting template.
-
Add the Language Model core component to your flow, and then enter your OpenAI API key.
This example uses the Language Model core component's default OpenAI model. If you want to use a different provider or model, edit the Model Provider, Model Name, and API Key fields accordingly.
My preferred provider or model isn't listedIf you want to use a provider or model that isn't built-in to the Language Model core component, you can replace this component with any additional language model.
Browse Bundles or Search for your preferred provider to find additional language models.
-
In the component's header menu, click Controls, enable the System Message parameter, and then click Close.
-
Add a Prompt Template component to your flow.
-
In the Template field, enter some instructions for the LLM, such as
You are an expert in geography who is tutoring high school students. -
Connect the Prompt Template component's output to the Language Model component's System Message input.
-
Add Chat Input and Chat Output components to your flow. These components are required for direct chat interaction with an LLM.
-
Connect the Chat Input component to the Language Model component's Input, and then connect the Language Model component's Message output to the Chat Output component.
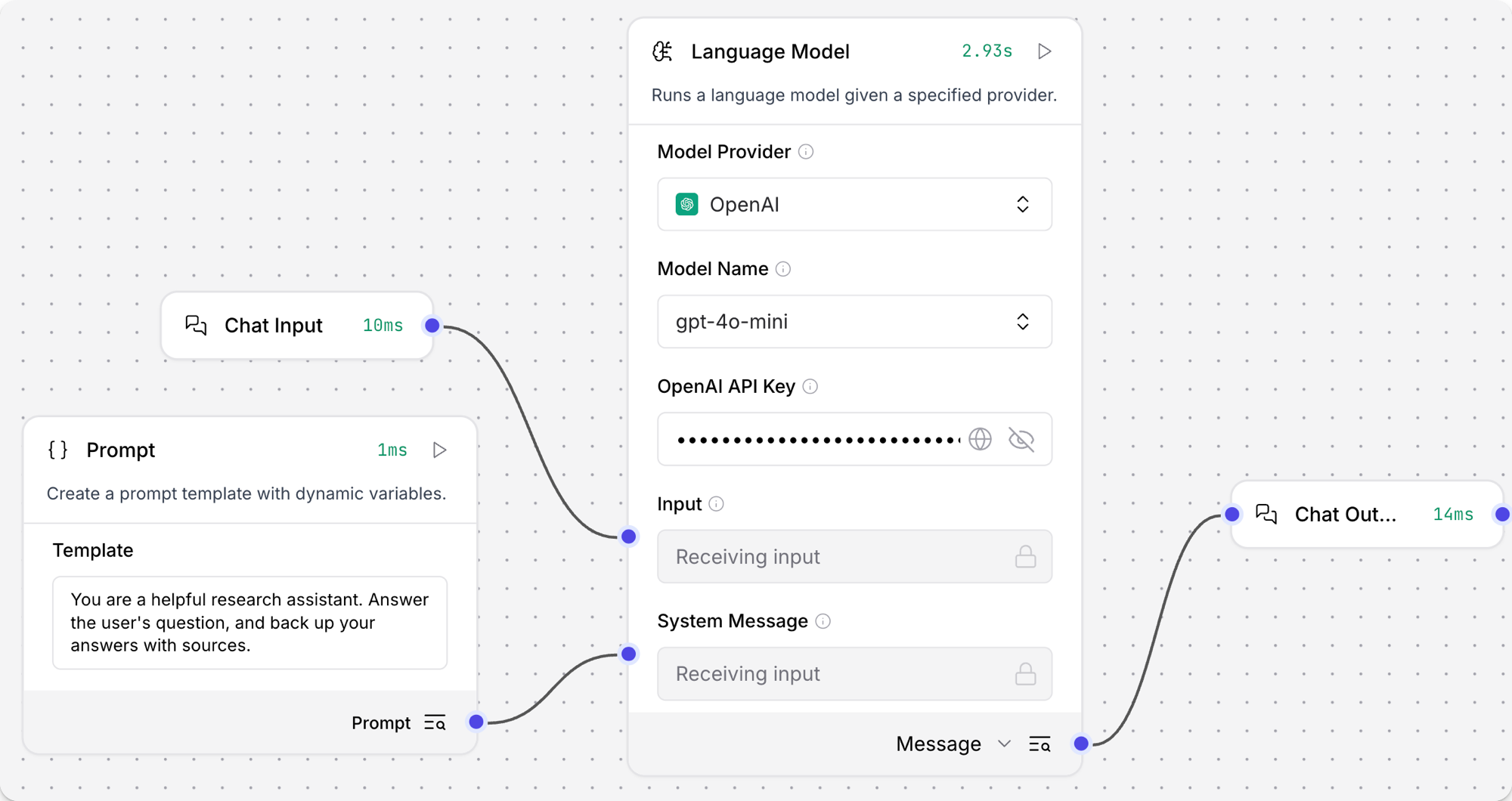
-
Open the Playground, and ask a question to chat with the LLM and test the flow, such as
What is the capital of Utah?.Result
The following response is an example of an OpenAI model's response. Your actual response may vary based on the model version at the time of your request, your template, and input.
_10The capital of Utah is Salt Lake City. It is not only the largest city in the state but also serves as the cultural and economic center of Utah. Salt Lake City was founded in 1847 by Mormon pioneers and is known for its proximity to the Great Salt Lake and its role in the history of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. For more information, you can refer to sources such as the U.S. Geological Survey or the official state website of Utah. -
Optional: Try a different model or provider to see how the response changes. For example, if you are using the Language Model core component, you could try an Anthropic model.
Then, open the Playground, ask the same question as you did before, and then compare the content and format of the responses.
This helps you understand how different models handle the same request so you can choose the best model for your use case. You can also learn more about different models in each model provider's documentation.
Result
The following response is an example of an Anthropic model's response. Your actual response may vary based on the model version at the time of your request, your template, and input.
Note that this response is shorter and includes sources, whereas the previous OpenAI response was more encyclopedic and didn't cite sources.
_10The capital of Utah is Salt Lake City. It is also the most populous city in the state. Salt Lake City has been the capital of Utah since 1896, when Utah became a state._10Sources:_10Utah State Government Official Website (utah.gov)_10U.S. Census Bureau_10Encyclopedia Britannica
Some components use a language model component to perform LLM-driven actions. Typically, these components prepare data for further processing by downstream components, rather than emitting direct chat output. For an example, see the Smart Transform component.
A component must accept a LanguageModel input to use a language model component as a driver, and you must set the language model component's output type to LanguageModel.
For more information, see Language Model output types.
If you don't want to use the Agent component's built-in LLMs, you can use a language model component to connect your preferred model:
-
Add a language model component to your flow.
You can use the Language Model core component or browse Bundles to find additional language models. Components in bundles may not have
language modelin the name. For example, Azure OpenAI LLMs are provided through the Azure OpenAI component. -
Configure the language model component as needed to connect to your preferred model.
-
Change the language model component's output type from Model Response to Language Model. The output port changes to a
LanguageModelport. This is required to connect the language model component to the Agent component. For more information, see Language Model output types. -
Add an Agent component to the flow, and then set Model Provider to Connect other models.
The Model Provider field changes to a Language Model (
LanguageModel) input. -
Connect the language model component's output to the Agent component's Language Model input. The Agent component now inherits the language model settings from the connected language model component instead of using any of the built-in models.
Language model parameters
The following parameters are for the Language Model core component. Other language model components can have additional or different parameters.
Some parameters are hidden by default in the visual editor. You can modify all parameters through the Controls in the component's header menu.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| provider | String | Input parameter. The model provider to use. |
| model_name | String | Input parameter. The name of the model to use. Options depend on the selected provider. |
| api_key | SecretString | Input parameter. The API Key for authentication with the selected provider. |
| input_value | String | Input parameter. The input text to send to the model. |
| system_message | String | Input parameter. A system message that helps set the behavior of the assistant. |
| stream | Boolean | Input parameter. Whether to stream the response. Default: false. |
| temperature | Float | Input parameter. Controls randomness in responses. Range: [0.0, 1.0]. Default: 0.1. |
| model | LanguageModel | Output parameter. Alternative output type to the default Message output. Produces an instance of Chat configured with the specified parameters. See Language Model output types. |
Language model output types
Language model components, including the core component and bundled components, can produce two types of output:
-
Model Response: The default output type emits the model's generated response as
Messagedata. Use this output type when you want the typical LLM interaction where the LLM produces a text response based on given input. -
Language Model: Change the language model component's output type to
LanguageModelwhen you need to attach an LLM to another component in your flow, such as an Agent or Smart Transform component.With this configuration, the language model component supports an action completed by another component, rather than a direct chat interaction. For an example, the Smart Transform component uses an LLM to create a function from natural language input.
Additional language models
If your provider or model isn't supported by the Language Model core component, additional language model components are available in Bundles.
You can use these components in the same way that you use the core Language Model component, as explained in Use language model components in flows.
Pair models with vector stores
By design, vector data is essential for LLM applications, such as chatbots and agents.
While you can use an LLM alone for generic chat interactions and common tasks, you can take your application to the next level with context sensitivity (such as RAG) and custom datasets (such as internal business data). This often requires integrating vector databases and vector searches that provide the additional context and define meaningful queries.
Langflow includes vector store components that can read and write vector data, including embedding storage, similarity search, Graph RAG traversals, and dedicated search instances like OpenSearch. Because of their interdependent functionality, it is common to use vector store, language model, and embedding model components in the same flow or in a series of dependent flows.
To find available vector store components, browse Bundles or Search for your preferred vector database provider.
Example: Vector search flow
For a tutorial that uses vector data in a flow, see Create a vector RAG chatbot.
The following example demonstrates how to use vector store components in flows alongside related components like embedding model and language model components. These steps walk through important configuration details, functionality, and best practices for using these components effectively. This is only one example; it isn't a prescriptive guide to all possible use cases or configurations.
-
Create a flow with the Vector Store RAG template.
This template has two subflows. The Load Data subflow loads embeddings and content into a vector database, and the Retriever subflow runs a vector search to retrieve relevant context based on a user's query.
-
Configure the database connection for both Astra DB components, or replace them with another pair of vector store components of your choice. Make sure the components connect to the same vector store, and that the component in the Retriever subflow is able to run a similarity search.
The parameters you set in each vector store component depend on the component's role in your flow. In this example, the Load Data subflow writes to the vector store, whereas the Retriever subflow reads from the vector store. Therefore, search-related parameters are only relevant to the Vector Search component in the Retriever subflow.
For information about specific parameters, see the documentation for your chosen vector store component.
-
To configure the embedding model, do one of the following:
-
Use an OpenAI model: In both OpenAI Embeddings components, enter your OpenAI API key. You can use the default model or select a different OpenAI embedding model.
-
Use another provider: Replace the OpenAI Embeddings components with another pair of embedding model components of your choice, and then configure the parameters and credentials accordingly.
-
Use Astra DB vectorize: If you are using an Astra DB vector store that has a vectorize integration, you can remove both OpenAI Embeddings components. If you do this, the vectorize integration automatically generates embeddings from the Ingest Data (in the Load Data subflow) and Search Query (in the Retriever subflow).
tipIf your vector store already contains embeddings, make sure your embedding model components use the same model as your previous embeddings. Mixing embedding models in the same vector store can produce inaccurate search results.
-
-
Recommended: In the Split Text component, optimize the chunking settings for your embedding model. For example, if your embedding model has a token limit of 512, then the Chunk Size parameter must not exceed that limit.
Additionally, because the Retriever subflow passes the chat input directly to the vector store component for vector search, make sure that your chat input string doesn't exceed your embedding model's limits. For this example, you can enter a query that is within the limits; however, in a production environment, you might need to implement additional checks or preprocessing steps to ensure compliance. For example, use additional components to prepare the chat input before running the vector search, or enforce chat input limits in your application code.
-
In the Language Model component, enter your OpenAI API key, or select a different provider and model to use for the chat portion of the flow.
-
Run the Load Data subflow to populate your vector store. In the Read File component, select one or more files, and then click Run component on the vector store component in the Load Data subflow.
The Load Data subflow loads files from your local machine, chunks them, generates embeddings for the chunks, and then stores the chunks and their embeddings in the vector database.
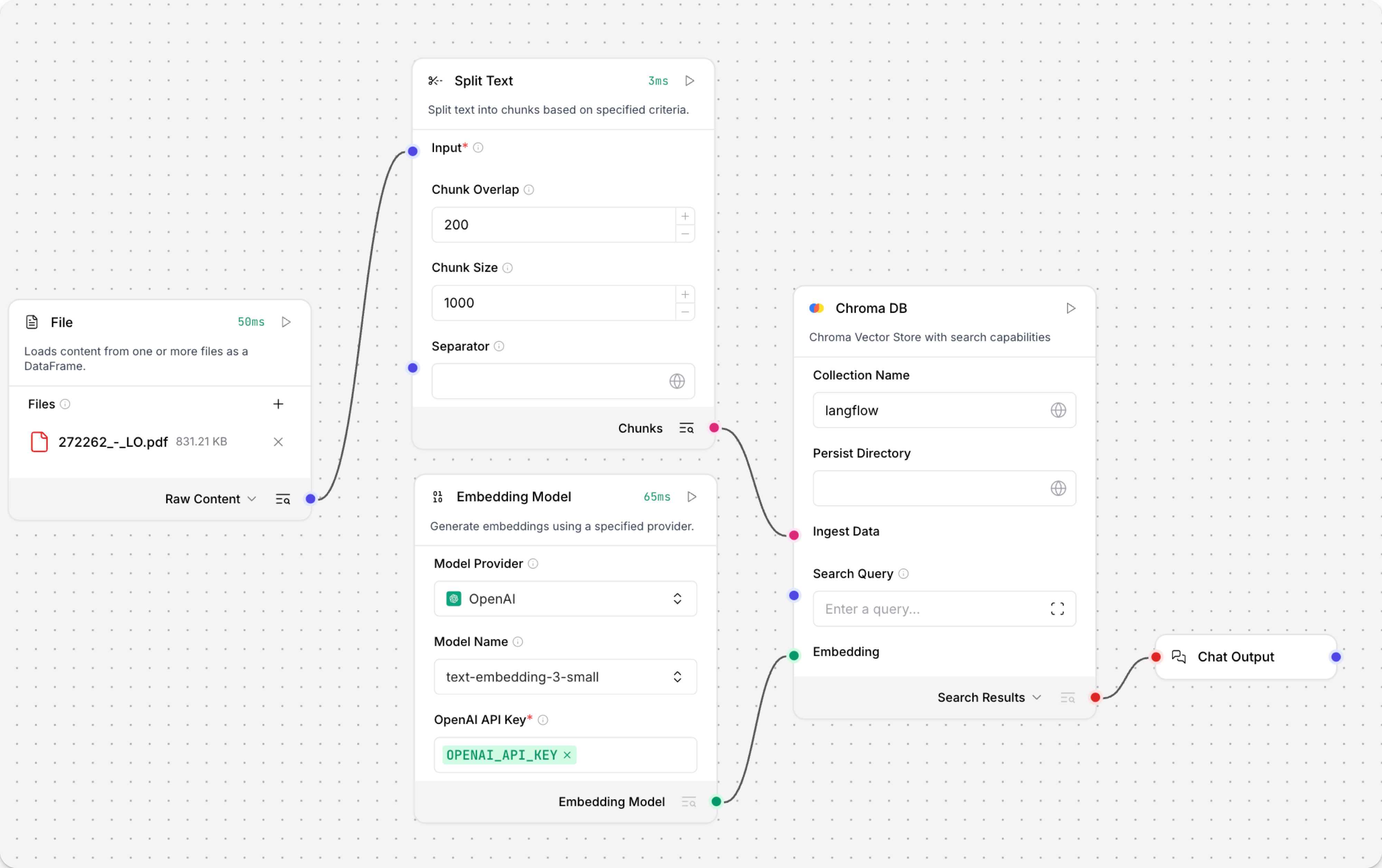
The Load Data subflow is separate from the Retriever subflow because you probably won't run it every time you use the chat. You can run the Load Data subflow as needed to preload or update the data in your vector store. Then, your chat interactions only use the components that are necessary for chat.
If your vector store already contains data that you want to use for vector search, then you don't need to run the Load Data subflow.
-
Open the Playground and start chatting to run the Retriever subflow.
The Retriever subflow generates an embedding from chat input, runs a vector search to retrieve similar content from your vector store, parses the search results into supplemental context for the LLM, and then uses the LLM to generate a natural language response to your query. The LLM uses the vector search results along with its internal training data and tools, such as basic web search and datetime information, to produce the response.
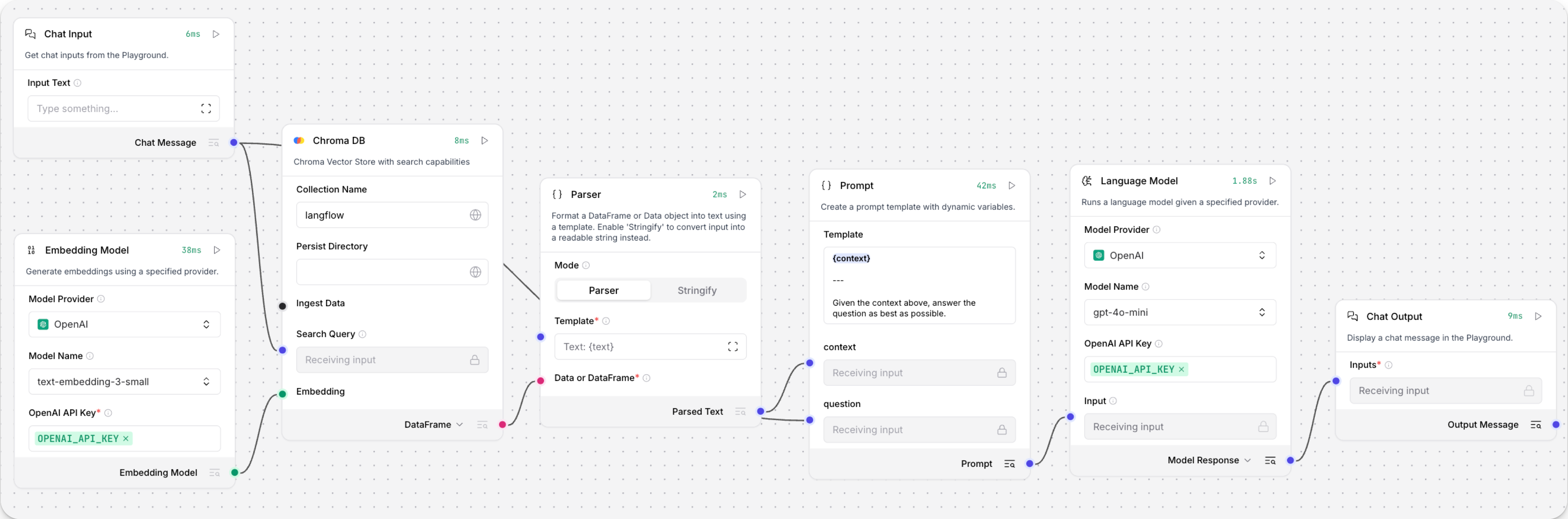
To avoid passing the entire block of raw search results to the LLM, the Parser component extracts
textstrings from the search resultsDataobject, and then passes them to the Prompt Template component inMessageformat. From there, the strings and other template content are compiled into natural language instructions for the LLM.You can use other components for this transformation, such as the Data Operations component, depending on how you want to use the search results.
To view the raw search results, click Inspect output on the vector store component after running the Retriever subflow.