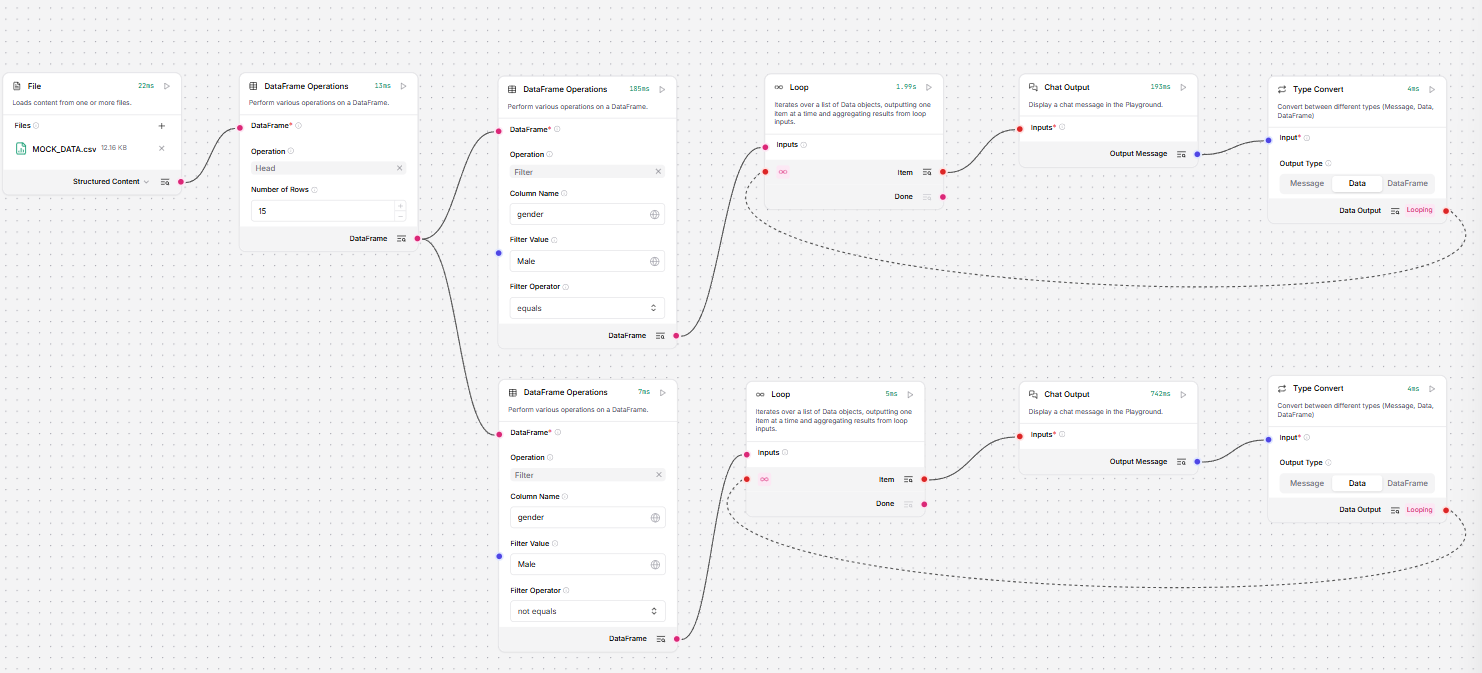
Loop
The Loop component iterates over a list of input by passing individual items to other components attached at the Item output port until there are no items left to process. Then, the Loop component passes the aggregated result of all looping to the component connected to the Done port.
The looping process
The Loop component is like a miniature flow within your flow. Here's a breakdown of the looping process:
-
Accepts a list of
DataorDataFrameobjects, such as a CSV file, through the Loop component's Inputs port. -
Splits the input into individual items. For example, a CSV file is broken down by rows.
Specifically, the Loop component repeatedly extracts items by
textkey in theDataorDataFrameobjects until there are no more items to extract. Eachitemoutput is aDataobjects. -
Iterates over each
itemby passing them to the Item output port.This port connects to one or more components that perform actions on each item. The final component in the Item loop connects back to the Loop component's Looping port to process the next item.
Only one component connects to the Item port, but you can pass the data through as many components as you need, as long as the last component in the chain connects back to the Looping port.
The If-Else component isn't compatible with the Loop component. For more information, see Conditional looping.
-
After processing all items, the results are aggregated into a single
Dataobject that is passed from the Loop component's Done port to the next component in the flow.
The following simplified Python code summarizes how the Loop component works. This isn't the actual component code; it is only meant to help you understand the general process.
_10for i in input: # Receive input data as a list_10 process_item(i) # Process each item through components connected at the Item port_10 if has_more_items():_10 continue # Loop back to Looping port to process the next item_10 else:_10 break # Exit the loop when no more items are left_10_10done = aggregate_results() # Compile all returned items_10_10print(done) # Send the aggregated results from the Done port to another component
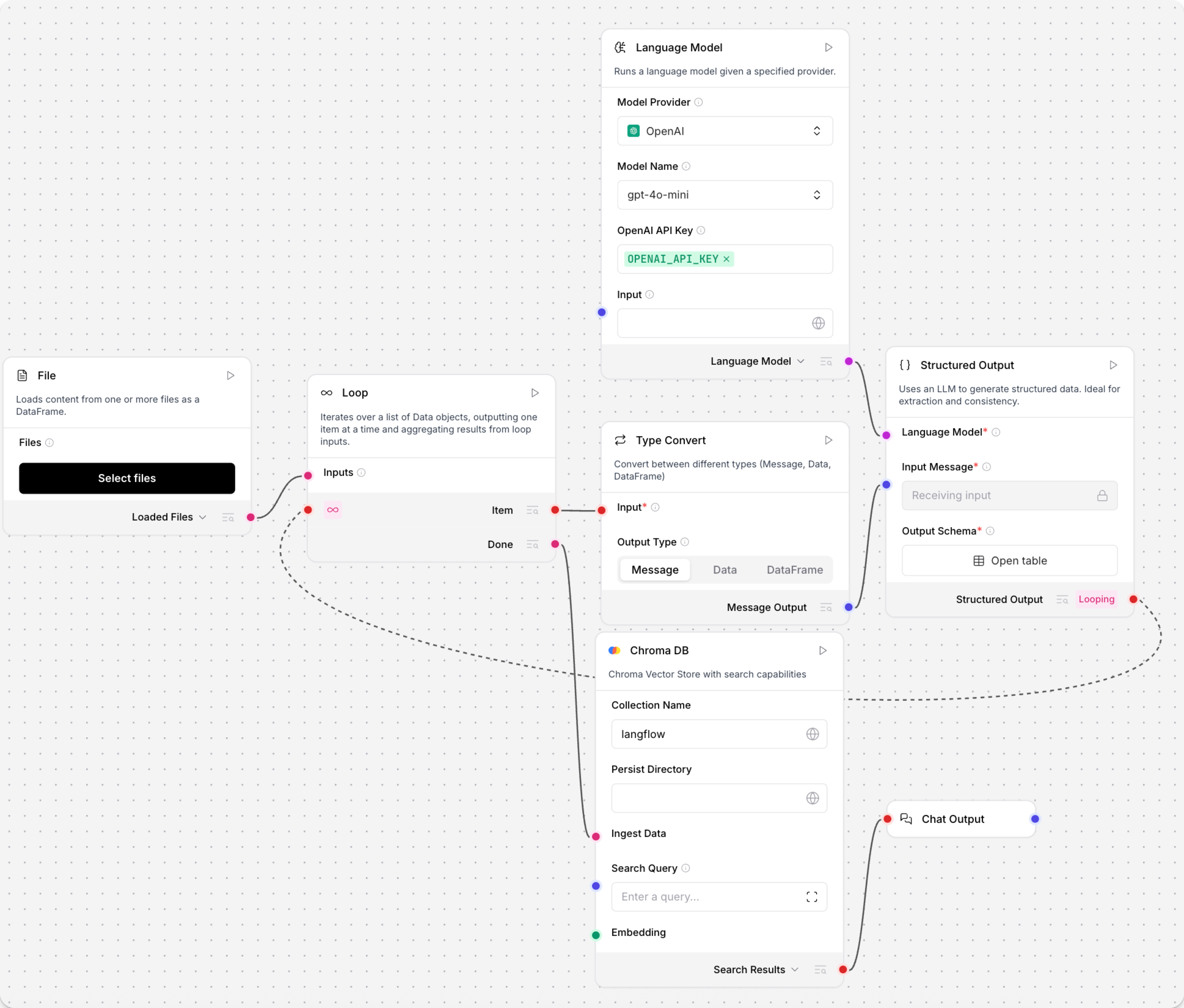
Loop example
In the follow example, the Loop component iterates over a CSV file until there are no rows left to process.
In this case, the Item port passes each row to a Type Convert component to convert the row into a Message object, passes the Message to a Structured Output component to be processed into structured data that is then passed back to the Loop component's Looping port.
After processing all rows, the Loop component loads the aggregated list of structured data into a Chroma DB database through the Chroma DB component connected to the Done port.
For more examples of the Loop component, try the Research Translation Loop template in Langflow, or see the video tutorial Mastering the Loop Component & Agentic RAG in Langflow.
Conditional looping
The If-Else component isn't compatible with the Loop component.
If you need conditional loop events, redesign your flow to process conditions before the loop.
For example, if you are looping over a DataFrame, you could use multiple DataFrame Operations components to conditionally filter data, and then run separate loops on each set of filtered data.