DataFrame Operations
The DataFrame Operations component performs operations on DataFrame (table) rows and columns, including schema changes, record changes, sorting, and filtering.
For all options, see DataFrame Operations parameters.
The output is a new DataFrame containing the modified data after running the selected operation.
Use the DataFrame Operations component in a flow
The following steps explain how to configure a DataFrame Operations component in a flow.
You can follow along with an example or use your own flow.
The only requirement is that the preceding component must create DataFrame output that you can pass to the DataFrame Operations component.
-
Create a new flow or use an existing flow.
Example: API response extraction flow
The following example flow uses five components to extract
Datafrom an API response, transform it to aDataFrame, and then perform further processing on the tabular data using a DataFrame Operations component. The sixth component, Chat Output, is optional in this example. It only serves as a convenient way for you to view the final output in the Playground, rather than inspecting the component logs.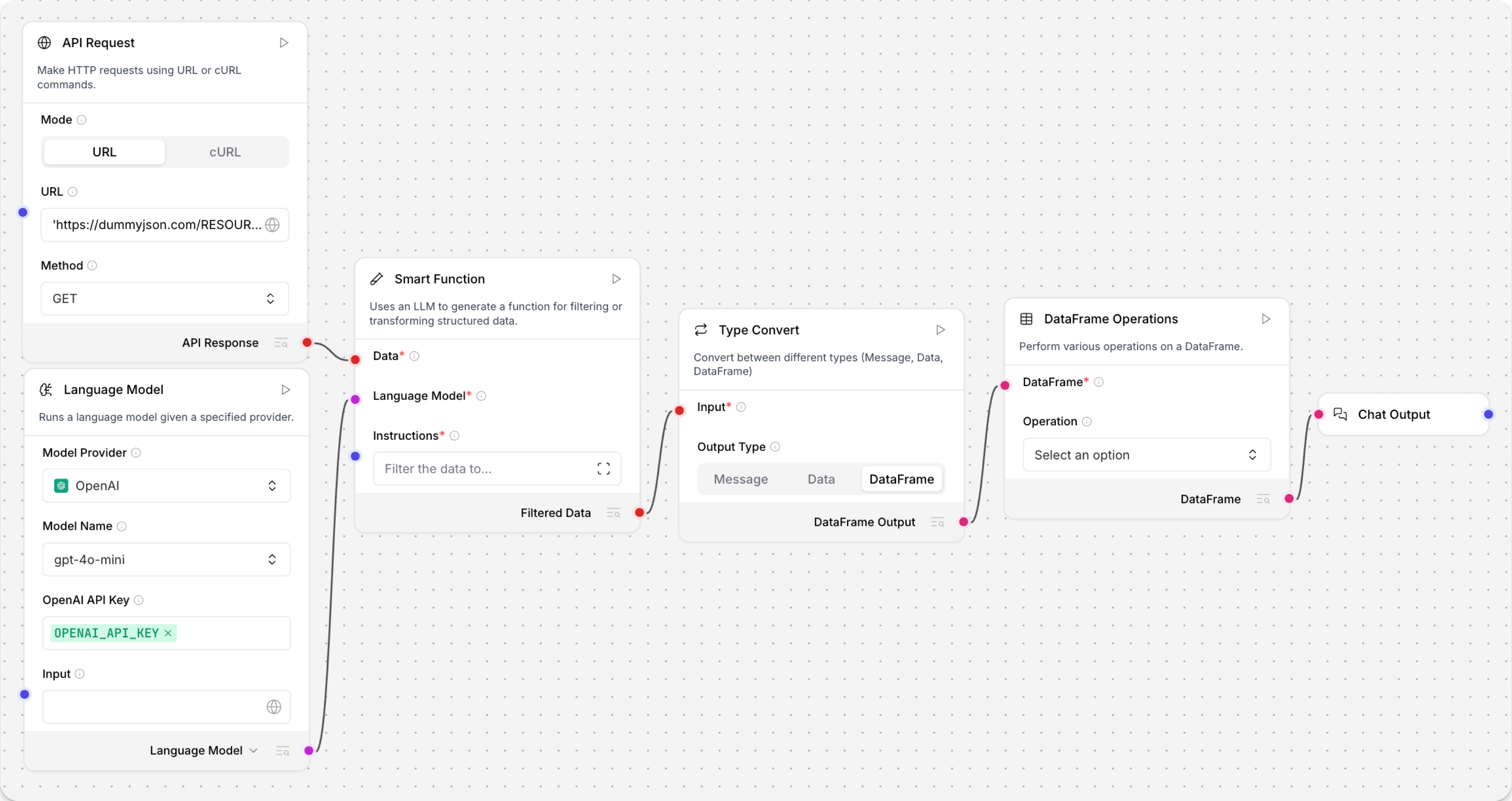
If you want to use this example to test the DataFrame Operations component, do the following:
-
Create a flow with the following components:
- API Request
- Language Model
- Smart Transform
- Type Convert
-
Configure the Smart Transform component and its dependencies:
- API Request: Configure the API Request component to get JSON data from an endpoint of your choice, and then connect the API Response output to the Smart Transform component's Data input.
- Language Model: Select your preferred provider and model, and then enter a valid API key.
Change the output to Language Model, and then connect the
LanguageModeloutput to the Smart Transform component's Language Model input. - Smart Transform: In the Instructions field, enter natural language instructions to extract data from the API response.
Your instructions depend on the response content and desired outcome.
For example, if the response contains a large
resultfield, you might provide instructions likeexplode the result field out into a Data object.
-
Convert the Smart Transform component's
Dataoutput toDataFrame:- Connect the Filtered Data output to the Type Convert component's Data input.
- Set the Type Convert component's Output Type to DataFrame.
Now the flow is ready for you to add the DataFrame Operations component.
-
-
Add a DataFrame Operations component to the flow, and then connect
DataFrameoutput from another component to the DataFrame input.All operations in the DataFrame Operations component require at least one
DataFrameinput from another component. If a component doesn't produceDataFrameoutput, you can use another component, such as the Type Convert component, to reformat the data before passing it to the DataFrame Operations component. Alternatively, you could consider using a component that is designed to process the original data type, such as the Parser component or Data Operations component.If you are following along with the example flow, connect the Type Convert component's DataFrame Output port to the DataFrame input.
-
In the Operations field, select the operation you want to perform on the incoming
DataFrame. For example, the Filter operation filters the rows based on a specified column and value.tipYou can select only one operation. If you need to perform multiple operations on the data, you can chain multiple DataFrame Operations components together to execute each operation in sequence. For more complex multi-step operations, like dramatic schema changes or pivots, consider using an LLM-powered component, like the Structured Output component or Smart Transform component, as a replacement or preparation for the DataFrame Operations component.
If you're following along with the example flow, select any operation that you want to apply to the data that was extracted by the Smart Transform component. To view the contents of the incoming
DataFrame, click Run component on the Type Convert component, and then Inspect output. If theDataFrameseems malformed, click Inspect output on each upstream component to determine where the error occurs, and then modify your flow's configuration as needed. For example, if the Smart Transform component didn't extract the expected fields, modify your instructions or verify that the given fields are present in the API Response output. -
Configure the operation's parameters. The specific parameters depend on the selected operation. For example, if you select the Filter operation, you must define a filter condition using the Column Name, Filter Value, and Filter Operator parameters. For more information, see DataFrame Operations parameters
-
To test the flow, click Run component on the DataFrame Operations component, and then click Inspect output to view the new
DataFramecreated from the Filter operation.If you want to view the output in the Playground, connect the DataFrame Operations component's output to a Chat Output component, rerun the DataFrame Operations component, and then click Playground.
For another example, see Conditional looping.
DataFrame Operations parameters
Most DataFrame Operations parameters are conditional because they only apply to specific operations.
The only permanent parameters are DataFrame (df), which is the DataFrame input, and Operation (operation), which is the operation to perform on the DataFrame.
Once you select an operation, the conditional parameters for that operation appear on the DataFrame Operations component.
- Add Column
- Drop Column
- Filter
- Head
- Rename Column
- Replace Value
- Select Columns
- Sort
- Tail
- Drop Duplicates
The Add Column operation allows you to add a new column to the DataFrame with a constant value.
The parameters are New Column Name (new_column_name) and New Column Value (new_column_value).
The Drop Column operation allows you to remove a column from the DataFrame, specified by Column Name (column_name).
The Filter operation allows you to filter the DataFrame based on a specified condition.
The output is a DataFrame containing only the rows that matched the filter condition.
Provide the following parameters:
- Column Name (
column_name): The name of the column to filter on. - Filter Value (
filter_value): The value to filter on. - Filter Operator (
filter_operator): The operator to use for filtering, one ofequals(default),not equals,contains,not contains,starts with,ends with,greater than, orless than.
The Head operation allows you to retrieve the first n rows of the DataFrame, where n is set in Number of Rows (num_rows).
The default is 5.
The output is a DataFrame containing only the selected rows.
The Rename Column operation allows you to rename an existing column in the DataFrame.
The parameters are Column Name (column_name), which is the current name, and New Column Name (new_column_name).
The Replace Value operation allows you to replace values in a specific column of the DataFrame.
This operation replaces a target value with a new value.
All cells matching the target value are replaced with the new value in the new DataFrame output.
Provide the following parameters:
- Column Name (
column_name): The name of the column to modify. - Value to Replace (
replace_value): The value that you want to replace. - Replacement Value (
replacement_value): The new value to use.
The Select Columns operation allows you to select one or more specific columns from the DataFrame.
Provide a list of column names in Columns to Select (columns_to_select).
In the visual editor, click Add More to add multiple fields, and then enter one column name in each field.
The output is a DataFrame containing only the specified columns.
The Sort operation allows you to sort the DataFrame on a specific column in ascending or descending order.
Provide the following parameters:
- Column Name (
column_name): The name of the column to sort on. - Sort Ascending (
ascending): Whether to sort in ascending or descending order. If enabled (true), sorts in ascending order; if disabled (false), sorts in descending order. Default: Enabled (true)
The Tail operation allows you to retrieve the last n rows of the DataFrame, where n is set in Number of Rows (num_rows).
The default is 5.
The output is a DataFrame containing only the selected rows.
The Drop Duplicates operation removes rows from the DataFrame by identifying all duplicate values within a single column.
The only parameter is the Column Name (column_name).
When the flow runs, all rows with duplicate values in the given column are removed.
The output is a DataFrame containing all columns from the original DataFrame, but only rows with non-duplicate values.