Python Interpreter
This component allows you to execute Python code with imported packages.
The Python Interpreter component can only import packages that are already installed in your Langflow environment.
If you encounter an ImportError when trying to use a package, you need to install it first.
To install custom packages, see Install custom dependencies.
Use the Python Interpreter in a flow
- To use this component in a flow, in the Global Imports field, add the packages you want to import as a comma-separated list, such as
math,pandas. At least one import is required. - In the Python Code field, enter the Python code you want to execute. Use
print()to see the output. - Optional: Enable Tool Mode, and then connect the Python Interpreter component to an Agent component as a tool.
For example, connect a Python Interpreter component and a Calculator component as tools for an Agent component, and then test how it chooses different tools to solve math problems.
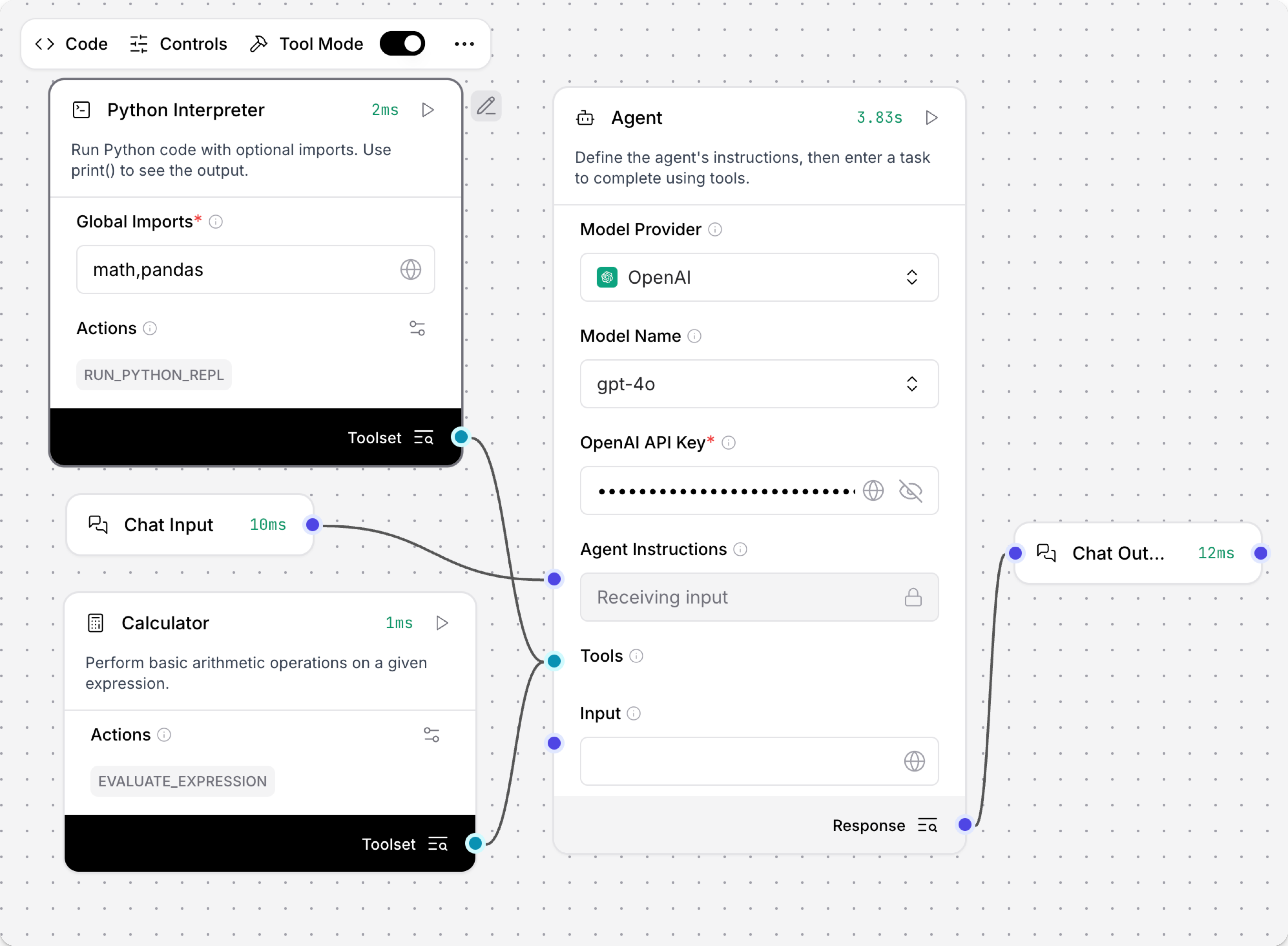
- Ask the agent an easier math question.
The Calculator tool can add, subtract, multiple, divide, or perform exponentiation.
The agent executes the
evaluate_expressiontool to correctly answer the question.
Result:
_10Executed evaluate_expression_10Input:_10{_10 "expression": "2+5"_10}_10Output:_10{_10 "result": "7"_10}
- Give the agent complete Python code.
This example creates a Pandas DataFrame table with the imported
pandaspackages, and returns the square root of the mean squares.
_12import pandas as pd_12import math_12_12# Create a simple DataFrame_12df = pd.DataFrame({_12 'numbers': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],_12 'squares': [x**2 for x in range(1, 6)]_12})_12_12# Calculate the square root of the mean_12result = math.sqrt(df['squares'].mean())_12print(f"Square root of mean squares: {result}")
The agent correctly chooses the run_python_repl tool to solve the problem.
Result:
_12Executed run_python_repl_12_12Input:_12_12{_12 "python_code": "import pandas as pd\nimport math\n\n# Create a simple DataFrame\ndf = pd.DataFrame({\n 'numbers': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],\n 'squares': [x**2 for x in range(1, 6)]\n})\n\n# Calculate the square root of the mean\nresult = math.sqrt(df['squares'].mean())\nprint(f\"Square root of mean squares: {result}\")"_12}_12Output:_12_12{_12 "result": "Square root of mean squares: 3.3166247903554"_12}
If you don't include the package imports in the chat, the agent can still create the table using pd.DataFrame, because the pandas package is imported globally by the Python Interpreter component in the Global Imports field.
Pass inputs to the Python Interpreter
To pass inputs to the Python Interpreter component, you need to customize the component's code to add input fields. After the input field is added to the component code, the port becomes available for connections. For example, to connect a Text component and pass a URL value to the Python Interpreter component, do the following:
-
Add a Python Interpreter component to your flow.
-
To modify the Python Interpreter component's code, click Edit Code.
-
To pass a URL input to the Python Interpreter component, make the following changes to the code:
a. Add the URL input field to the
inputslist. This creates the input port that other components can connect to.b. Update the
get_globalsmethod to extract the URL value and add it to the globals dictionary. This makes theurlvariable available in the component's Python code.c. Update the default Python code value to use the
urlvariable.The following example demonstrates these modifications.
Python code example
_121import importlib_121_121from langchain_experimental.utilities import PythonREPL_121from lfx.custom.custom_component.component import Component_121from lfx.io import MultilineInput, Output, StrInput_121from lfx.schema.data import Data_121from lfx.schema.message import Message # Needed to extract text from Message objects_121_121class PythonREPLComponent(Component):_121display_name = "Python Interpreter"_121description = "Run Python code with optional imports. Use print() to see the output."_121documentation: str = "https://docs.langflow.org/python-interpreter"_121icon = "square-terminal"_121_121inputs = [_121StrInput(_121name="global_imports",_121display_name="Global Imports",_121info="A comma-separated list of modules to import globally, e.g. 'math,numpy,pandas'.",_121value="math,pandas",_121required=True,_121),_121MultilineInput(_121name="python_code",_121display_name="Python Code",_121info="The Python code to execute. Only modules specified in Global Imports can be used. Use 'url' variable if URL input is connected.",_121value="print(f'URL: {url}')", # Updated to make the URL variable available to the Python code execution_121input_types=["Message"],_121tool_mode=True,_121required=True,_121),_121# Add the URL input field to inputs list_121StrInput(_121name="url",_121display_name="URL",_121info="URL variable that can be used in Python code. Connect a Text component or enter manually.",_121value="",_121input_types=["Text", "Message"],_121required=False,_121),_121]_121_121outputs = [_121Output(_121display_name="Results",_121name="results",_121type_=Data,_121method="run_python_repl",_121),_121]_121_121def get_globals(self, global_imports: str | list[str]) -> dict:_121"""Create a globals dictionary with only the specified allowed imports and input variables."""_121global_dict = {}_121_121try:_121if isinstance(global_imports, str):_121modules = [module.strip() for module in global_imports.split(",")]_121elif isinstance(global_imports, list):_121modules = global_imports_121else:_121msg = "global_imports must be either a string or a list"_121raise TypeError(msg)_121_121for module in modules:_121try:_121imported_module = importlib.import_module(module)_121global_dict[imported_module.__name__] = imported_module_121except ImportError as e:_121msg = f"Could not import module {module}: {e!s}"_121raise ImportError(msg) from e_121_121# Add the URL variable to the component's globals dictionary_121# Extract from Message object or use the string directly_121if hasattr(self, "url") and self.url:_121url_value = self.url.text if isinstance(self.url, Message) else str(self.url)_121if url_value:_121global_dict["url"] = url_value # Makes 'url' available in Python code_121self.log(f"URL variable set: {url_value}")_121_121except Exception as e:_121self.log(f"Error in global imports: {e!s}")_121raise_121else:_121self.log(f"Successfully imported modules: {list(global_dict.keys())}")_121return global_dict_121_121def run_python_repl(self) -> Data:_121try:_121# Extract Python code text if it's a Message object_121python_code_text = self.python_code_121if isinstance(python_code_text, Message):_121python_code_text = python_code_text.text if python_code_text.text else ""_121elif not isinstance(python_code_text, str):_121python_code_text = str(python_code_text)_121_121globals_ = self.get_globals(self.global_imports)_121python_repl = PythonREPL(_globals=globals_)_121result = python_repl.run(python_code_text)_121result = result.strip() if result else ""_121_121self.log("Code execution completed successfully")_121return Data(data={"result": result})_121_121except ImportError as e:_121error_message = f"Import Error: {e!s}"_121self.log(error_message)_121return Data(data={"error": error_message})_121_121except SyntaxError as e:_121error_message = f"Syntax Error: {e!s}"_121self.log(error_message)_121return Data(data={"error": error_message})_121_121except (NameError, TypeError, ValueError) as e:_121error_message = f"Error during execution: {e!s}"_121self.log(error_message)_121return Data(data={"error": error_message})_121_121def build(self):_121return self.run_python_repl -
To save the modifications, click Check & Save.
-
Add a Text component to your flow and set its value, such as
google.com. -
Connect the Text component's output to the new URL input field on your customized Python Interpreter component.
The Python Interpreter component can now use the url variable in the Python code that it executes.
Python Interpreter parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| global_imports | String | Input parameter. A comma-separated list of modules to import globally, such as math,pandas,numpy. |
| python_code | Code | Input parameter. The Python code to execute. Only modules specified in Global Imports can be used. |
| results | Data | Output parameter. The output of the executed Python code, including any printed results or errors. |