SQL Database
The SQL Database component executes SQL queries on SQLAlchemy-compatible databases. It supports any SQLAlchemy-compatible database, such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQLite.
For CQL queries, see the DataStax bundle.
Query an SQL database with natural language prompts
The following example demonstrates how to use the SQL Database component in a flow, and then modify the component to support natural language queries through an Agent component.
This allows you to use the same SQL Database component for any query, rather than limiting it to a single manually entered query or requiring the user, application, or another component to provide valid SQL syntax as input. Users don't need to master SQL syntax because the Agent component translates the users' natural language prompts into SQL queries, passes the query to the SQL Database component, and then returns the results to the user.
Additionally, input from applications and other components doesn't have to be extracted and transformed to exact SQL queries. Instead, you only need to provide enough context for the agent to understand that it should create and run a SQL query according to the incoming data.
-
Use your own sample database or create a test database.
Create a test SQL database
-
Create a database called
test.db:_10sqlite3 test.db -
Add some values to the database:
_13sqlite3 test.db "_13CREATE TABLE users (_13id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,_13name TEXT,_13email TEXT,_13age INTEGER_13);_13_13INSERT INTO users (name, email, age) VALUES_13('John Doe', 'john@example.com', 30),_13('Jane Smith', 'jane@example.com', 25),_13('Bob Johnson', 'bob@example.com', 35);_13" -
Verify that the database has been created and contains your data:
_10sqlite3 test.db "SELECT * FROM users;"The result should list the text data you entered in the previous step:
_101|John Doe|john@example.com_102|Jane Smith|jane@example.com_103|John Doe|john@example.com_104|Jane Smith|jane@example.com
-
-
Add an SQL Database component to your flow.
-
In the Database URL field, add the connection string for your database, such as
sqlite:///test.db.At this point, you can enter an SQL query in the SQL Query field or use the port to pass a query from another component, such as a Chat Input component. If you need more space, click Expand to open a full-screen text field.
However, to make this component more dynamic in an agentic context, use an Agent component to transform natural language input to SQL queries, as explained in the following steps.
-
Click the SQL Database component to expose the component's header menu, and then enable Tool Mode.
You can now use this component as a tool for an agent. In Tool Mode, no query is set in the SQL Database component because the agent will generate and send one if it determines that the tool is required to complete the user's request. For more information, see Configure tools for agents.
-
Add an Agent component to your flow, and then enter your OpenAI API key.
The default model is an OpenAI model. If you want to use a different model, edit the Model Provider, Model Name, and API Key fields accordingly.
If you need to execute highly specialized queries, consider selecting a model that is trained for tasks like advanced SQL queries. If your preferred model isn't in the Agent component's built-in model list, set Model Provider to Connect other models, and then connect any language model component.
-
Connect the SQL Database component's Toolset output to the Agent component's Tools input.
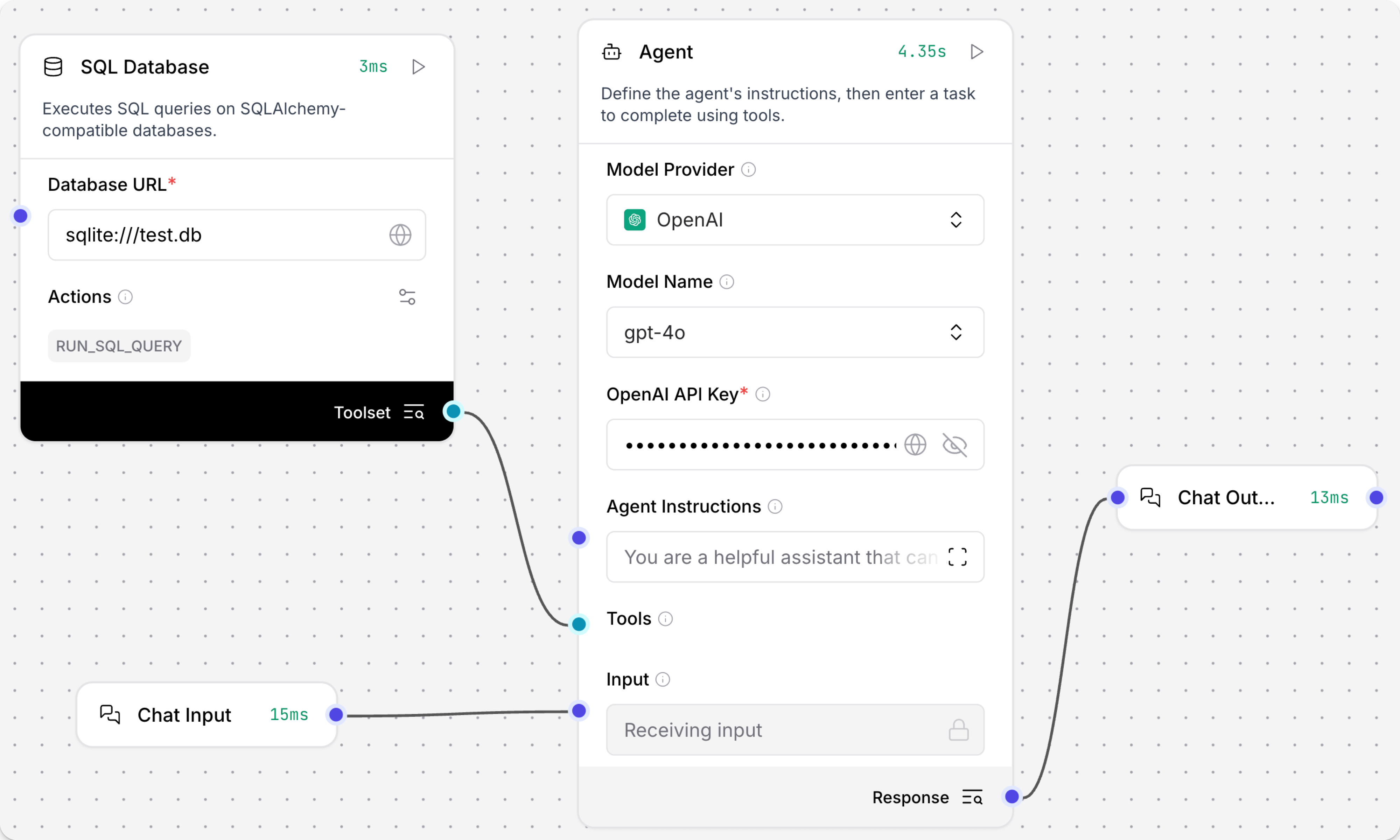
-
Click Playground, and then ask the agent a question about the data in your database, such as
Which users are in my database?The agent determines that it needs to query the database to answer the question, uses the LLM to generate an SQL query, and then uses the SQL Database component's
RUN_SQL_QUERYaction to run the query on your database. Finally, it returns the results in a conversational format, unless you provide instructions to return raw results or a different format.The following example queried a test database with little data, but with a more robust dataset you could ask more detailed or complex questions.
_10Here are the users in your database:_10_101. **John Doe** - Email: john@example.com_102. **Jane Smith** - Email: jane@example.com_103. **John Doe** - Email: john@example.com_104. **Jane Smith** - Email: jane@example.com_10_10It seems there are duplicate entries for the users.
SQL Database parameters
Some parameters are hidden by default in the visual editor. You can modify all component parameters through the component inspection panel that appears when you select a component.
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| database_url | Database URL | Input parameter. The SQLAlchemy-compatible database connection URL. |
| query | SQL Query | Input parameter. The SQL query to execute, which can be entered directly, passed in from another component, or, in Tool Mode, automatically provided by an Agent component. |
| include_columns | Include Columns | Input parameter. Whether to include column names in the result. The default is enabled (true). |
| add_error | Add Error | Input parameter. If enabled, adds any error messages to the result, if any are returned. The default is disabled (false). |
| run_sql_query | Result Table | Output parameter. The query results as a DataFrame. |