NVIDIA
Bundles contain custom components that support specific third-party integrations with Langflow.
This page describes the components that are available in the NVIDIA bundle.
NVIDIA
This component generates text using NVIDIA LLMs. For more information about NVIDIA LLMs, see the NVIDIA AI documentation.
NVIDIA parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max_tokens | Integer | Input parameter. The maximum number of tokens to generate. Set to 0 for unlimited tokens. |
| model_name | String | Input parameter. The name of the NVIDIA model to use. Default: mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1. |
| base_url | String | Input parameter. The base URL of the NVIDIA API. Default: https://integrate.api.nvidia.com/v1. |
| nvidia_api_key | SecretString | Input parameter. The NVIDIA API Key for authentication. |
| temperature | Float | Input parameter. Controls randomness in the output. Default: 0.1. |
| seed | Integer | Input parameter. The seed controls the reproducibility of the job. Default: 1. |
| model | LanguageModel | Output parameter. An instance of ChatNVIDIA configured with the specified parameters. |
NVIDIA NIM on WSL2
NVIDIA NIM (NVIDIA Inference Microservices) provides containers to self-host GPU-accelerated inferencing microservices.
You can use the NVIDIA component to connect Langflow with NVIDIA NIM on an RTX Windows system with Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2) installed.
The following example connects an NVIDIA language model component in Langflow to a deployed mistral-nemo-12b-instruct NIM on an RTX Windows system with WSL2.
-
Prepare your system:
-
A NIM container deployed according to the model's instructions
Prerequisites vary between models. For example, to deploy the
mistral-nemo-12b-instructNIM, follow the instructions for Windows on RTX AI PCs (Beta) on your model's deployment overview. -
Windows 11 build 23H2 or later
-
At least 12 GB of RAM
-
Create a flow based on the Basic Prompting template.
-
Replace the OpenAI model component with the NVIDIA component.
-
In the NVIDIA component's Base URL field, add the URL where your NIM is accessible. If you followed your model's deployment instructions, the value is
http://localhost:8000/v1. -
In the NVIDIA component's NVIDIA API Key field, add your NVIDIA API Key.
-
Select your model from the Model Name field.
-
Open the Playground and chat with your NIM model.
NVIDIA Embeddings
The NVIDIA Embeddings component generates embeddings using NVIDIA models.
For more information about using embedding model components in flows, see Embedding model components.
NVIDIA Embeddings parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| model | String | Input parameter. The NVIDIA model to use for embeddings, such as nvidia/nv-embed-v1. |
| base_url | String | Input parameter. The base URL for the NVIDIA API. Default: https://integrate.api.nvidia.com/v1. |
| nvidia_api_key | SecretString | Input parameter. The API key for authenticating with NVIDIA's service. |
| temperature | Float | Input parameter. The model temperature for embedding generation. Default: 0.1. |
| embeddings | Embeddings | Output parameter. An NVIDIAEmbeddings instance for generating embeddings. |
Be aware of your embedding model's chunk size limit. Tokenization errors can occur if your text chunks are too large. For more information, see Tokenization errors due to chunk size.
NVIDIA Rerank
This component finds and reranks documents using the NVIDIA API.
NVIDIA Retriever Extraction
The NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component integrates with the NVIDIA nv-ingest microservice for data ingestion, processing, and extraction of text files.
The nv-ingest service supports multiple extraction methods for PDF, DOCX, and PPTX file types, and includes pre- and post-processing services like splitting, chunking, and embedding generation. The extractor service's High Resolution mode uses the nemoretriever-parse extraction method for better quality extraction from scanned PDF documents. This feature is only available for PDF files.
The NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component imports the NVIDIA Ingestor client, ingests files with requests to the NVIDIA ingest endpoint, and outputs the processed content as a list of Data objects. Ingestor accepts additional configuration options for data extraction from other text formats. To configure these options, see the parameters.
NVIDIA Retriever Extraction is also known as NV-Ingest and NeMo Retriever Extraction.
Use the NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component in a flow
The NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component accepts Message inputs, and then outputs Data. The component calls an NVIDIA Ingest microservice's endpoint to ingest a local file and extract the text.
To use the NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component in your flow, follow these steps:
-
Prepare your system:
-
An NVIDIA Ingest endpoint. For more information on setting up an NVIDIA Ingest endpoint, see the NVIDIA Ingest quickstart.
-
The NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component requires the installation of additional dependencies to your Langflow environment. To install the dependencies in a virtual environment, run the following commands.
- If you have the Langflow repository cloned and installed from source:
_10source **YOUR_LANGFLOW_VENV**/bin/activate_10uv sync --extra nv-ingest_10uv run langflow run- If you are installing Langflow from the Python Package Index:
_10source **YOUR_LANGFLOW_VENV**/bin/activate_10uv pip install --prerelease=allow 'langflow[nv-ingest]'_10uv run langflow run
-
-
Add the NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component to your flow.
-
In the Base URL field, enter the URL of the NVIDIA Ingest endpoint. You can also store the URL as a global variable to reuse it in multiple components and flows.
-
Click Select Files to select a file to ingest.
-
Select which text type to extract from the file: text, charts, tables, images, or infographics.
-
Optional: For PDF files, enable High Resolution Mode for better quality extraction from scanned documents.
-
Select whether to split the text into chunks.
Some parameters are hidden by default in the visual editor. You can modify all component parameters through the component inspection panel that appears when you select a component.
-
Click Run component to ingest the file, and then click Logs or Inspect output to confirm the component ingested the file.
-
To store the processed data in a vector database, add a vector store component to your flow, and then connect the NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component's
Dataoutput to the vector store component's input.When you run the flow with a vector store component, the processed data is stored in the vector database. You can query your database to retrieve the uploaded data.
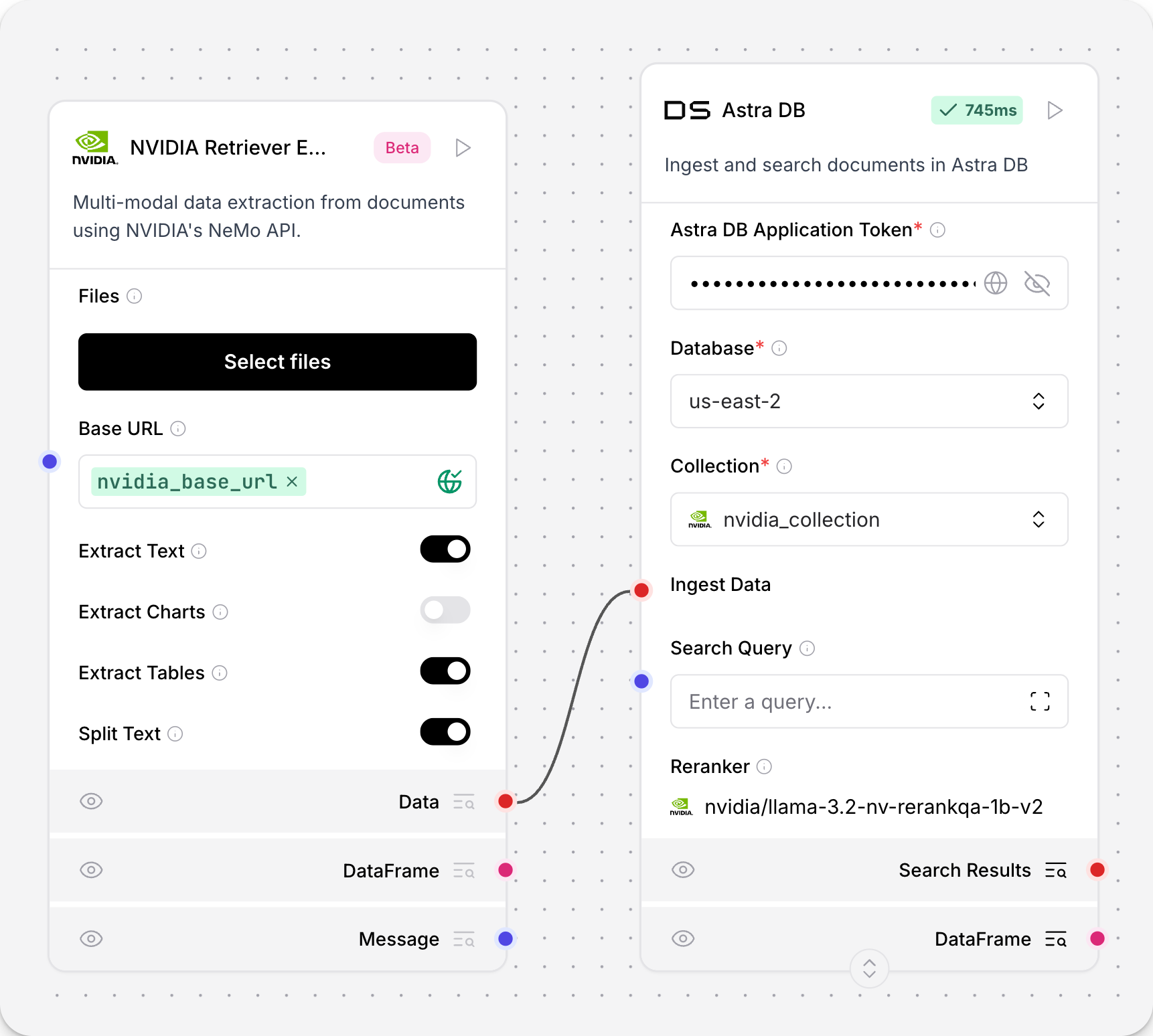
NVIDIA Retriever Extraction parameters
The NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component has the following parameters.
For more information, see the NV-Ingest documentation.
Inputs
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| base_url | NVIDIA Ingestion URL | The URL of the NVIDIA Ingestion API. |
| path | Path | File path to process. |
| extract_text | Extract Text | Extract text from documents. Default: true. |
| extract_charts | Extract Charts | Extract text from charts. Default: false. |
| extract_tables | Extract Tables | Extract text from tables. Default: true. |
| extract_images | Extract Images | Extract images from document. Default: true. |
| extract_infographics | Extract Infographics | Extract infographics from document. Default: false. |
| text_depth | Text Depth | The level at which text is extracted. Options: 'document', 'page', 'block', 'line', 'span'. Default: page. |
| split_text | Split Text | Split text into smaller chunks. Default: true. |
| chunk_size | Chunk Size | The number of tokens per chunk. Default: 500. Make sure the chunk size is compatible with your embedding model. For more information, see Tokenization errors due to chunk size. |
| chunk_overlap | Chunk Overlap | Number of tokens to overlap from previous chunk. Default: 150. |
| filter_images | Filter Images | Filter images (see advanced options for filtering criteria). Default: false. |
| min_image_size | Minimum Image Size Filter | Minimum image width/length in pixels. Default: 128. |
| min_aspect_ratio | Minimum Aspect Ratio Filter | Minimum allowed aspect ratio (width / height). Default: 0.2. |
| max_aspect_ratio | Maximum Aspect Ratio Filter | Maximum allowed aspect ratio (width / height). Default: 5.0. |
| dedup_images | Deduplicate Images | Filter duplicated images. Default: true. |
| caption_images | Caption Images | Generate captions for images using the NVIDIA captioning model. Default: true. |
| high_resolution | High Resolution (PDF only) | Process PDF in high-resolution mode for better quality extraction from scanned PDF. Default: false. |
Outputs
The NVIDIA Retriever Extraction component outputs a list of Data objects where each object contains:
text: The extracted content.- For text documents: The extracted text content.
- For tables and charts: The extracted table/chart content.
- For images: The image caption.
- For infographics: The extracted infographic content.
file_path: The source file name and path.document_type: The type of the document, which can betext,structured, orimage.description: Additional description of the content.
The output varies based on the document_type:
-
Documents with
document_type: "text"contain:- Raw text content extracted from documents, for example, paragraphs from PDFs or DOCX files.
- Content stored directly in the
textfield. - Content extracted using the
extract_textparameter.
-
Documents with
document_type: "structured"contain:- Text extracted from tables, charts, and infographics and processed to preserve structural information.
- Content extracted using the
extract_tables,extract_charts, andextract_infographicsparameters. - Content stored in the
textfield after being processed from thetable_contentmetadata.
-
Documents with
document_type: "image"contain:- Image content extracted from documents.
- Caption text stored in the
textfield whencaption_imagesis enabled. - Content extracted using the
extract_imagesparameter.
NVIDIA System-Assist
The NVIDIA System-Assist component integrates your flows with NVIDIA G-Assist, enabling interaction with NVIDIA GPU drivers through natural language prompts.
For example, prompt G-Assist with "What is my current GPU temperature?" or "Show me the available GPU memory" to get information, and then tell G-Assist to modify your GPU settings.
For more information, see the NVIDIA G-Assist repository.
-
Prepare your system:
- The NVIDIA System-Assist component requires an NVIDIA GPU on a Windows operating system.
- It uses the
gassist.risepackage, which is installed with all Langflow versions that include this component.
-
Create a flow with a Chat Input component, NVIDIA System-Assist component, and Chat Output components.
This is a simplified example that uses only three components. Depending on your use case, your flow might use more components or different inputs and outputs.
-
Connect the Chat Input component to the NVIDIA System-Assist component's Prompt input.
The Prompt parameter accepts a natural language prompt that is processed by the NVIDIA G-Assist AI Assistant. In this example, you'll provide the prompt as chat input. You could also enter a prompt directly in the Prompt input or connect another input component.
-
Connect the NVIDIA System-Assist component's output to the Chat Output component.
-
To test the flow, open the Playground, and then ask a question about your GPU. For example,
"What is my current GPU temperature?".Through the NVIDIA System-Assist component, NVIDIA G-Assist queries your GPU based on the prompt, and then prints the response to the Playground.
The component's output is a
Messagecontaining the NVIDIA G-Assist response. The string response with the completed operation result is available in thetextkey in theMessageobject.